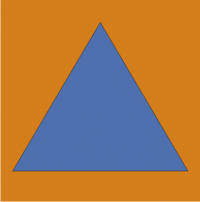
On 1864 twelve countries signed the 1st Geneva Convention on aid to people having suffered in armed conflicts. Russia signed the Convention on 1867- at that time Latvia was incorporated in Russia. After the Second World War on 12th August 1949 Diplomatic Conference in Geneva accepted the 4th Geneva Convention (valid from 1950) on protection of civilians – especially women and children and also property - during wartime. Convention is ratified by 195 countries, Latvia joined it on 20th November 1991. By 1st protocol 66th item 4th paragraph of the Convention international civil protection emblem – blue isosceles triangle on orange base - was confirmed.
Civil protection emblem
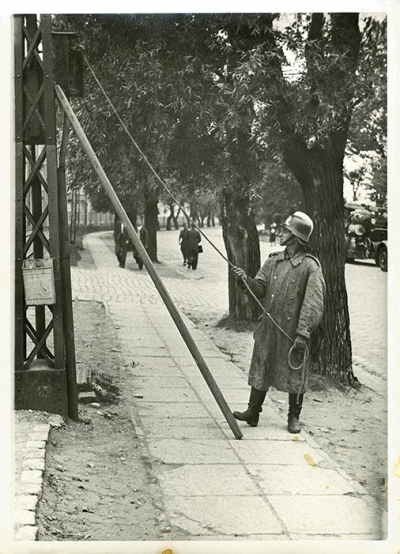
Passive anti-aircraft defense 1930s, 1940
Civil protection as a constituent part of state defence system has developed from passive anti-aircraft defense system introduced in Latvia in 1934 till nowadays. Its beginnings are connected with World War I (1914-1918) when aircrafts appeared and local anti-aircraft defense was organized in many countries.
Already at the beginning of 1930ies in Latvia several laws on passive anti-aircraft defense were adopted and instructions issued on defense against air attacks, supply of people with gas-masks, building of shelters.
The main tasks of local anti-aicraft defense were warning of inhabitants on enemy’s air-raids, securing of lighting in black out regime of objects and dwelling places, arranging bombshelters, securing aid to inhabitants and animals etc. Local anti-aircraft defense was subordinated to Ministry of Interior.
Riga Fire command IV department fire-fighter checking anti-aircraft protection alarms, 1939
To reduce civilian casualties in the event of enemy air attacks, the Passive Defence Against Air Attacks Act provided for the construction of safe rooms against gases and bombs - so-called shelters.
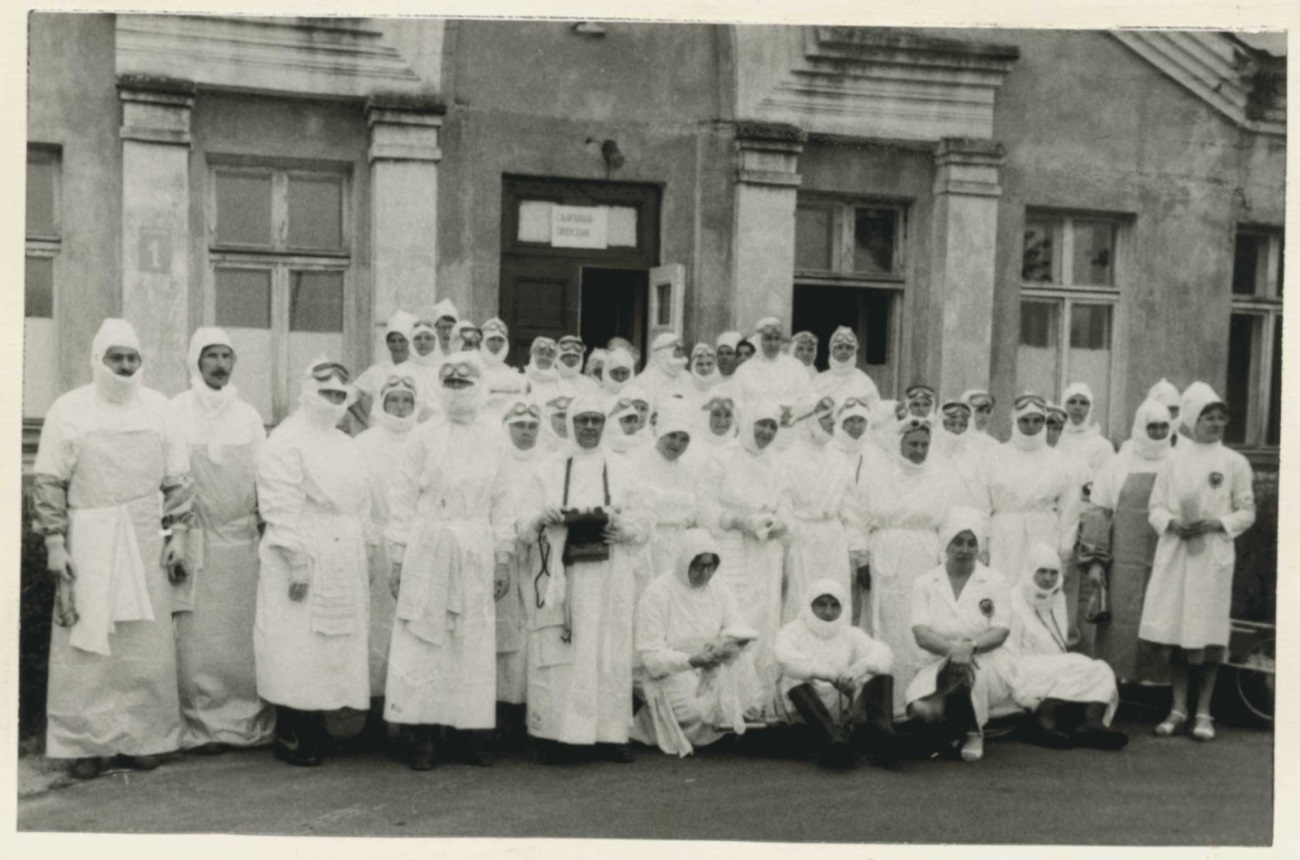
In the spring of 1937, the first modern shelter-ambulance with a capacity of 300 people was built in the new building of the Red Cross School of Sisters of Mercy in Riga, Jāņa Asara iela 3.
In September 1938, the gas shelter, built in the basement of the Ministry of the Interior, was opened to the public and was recommended as a model for householders who wanted to build shelters in their houses.
A shelter in the basement of the Ministry of the Interior, 1938.
On 28 September 1938, the President of the State and Prime Minister Kārlis Ulmanis promulgated the Law on Supplying the Population with Gas Masks. This was one of the most important laws in the "Self-Defense" system of passive defense against air attacks. In accordance with Article 2 of the Law, on 15 December 1938, the "Instruction to the Law on Supplying the Population with Gas Masks" was issued.
At the end of 1938, one of the largest state industrial enterprises, the State Electrotechnical Factory (VEF), started to manufacture People's gas masks. All the possibilities of a chemical attack were taken into account when designing the prototype of the gas mask.
Instructors were tasked with training people in self-defense and the use of gas masks, including care and storage of gas masks.
Gas-mask, produced on 1939 by VEF factory
Local anti-aircraft defense 1940s-1950s
On 26 September 1940, the Council of People's Commissars of the Latvian SSR adopted Decision No 216 on the subordination of the Passive Air Defense Board of the People's Commissariat of Internal Affairs of the Latvian SSR directly to the Council of People's Commissars of the Latvian SSR and it renaming as the Local Air Defense Board.
In December 1940, a decision was adopted on the establishment of a voluntary mass defense organisation - the Society for the Promotion of the Development of Defense, Aviation and Chemical Defense (abbreviated- Osoaviachima) in the Latvian SSR.
Osoaviachim's prepared specialists for individual and collective anti-air and anti-chemical defense (abbreviated - PVHO), later - for the norm "Ready for anti-air and chemical defense", and also prepared specialists for military defense.
Participants of OSAVIACHIM, 1944
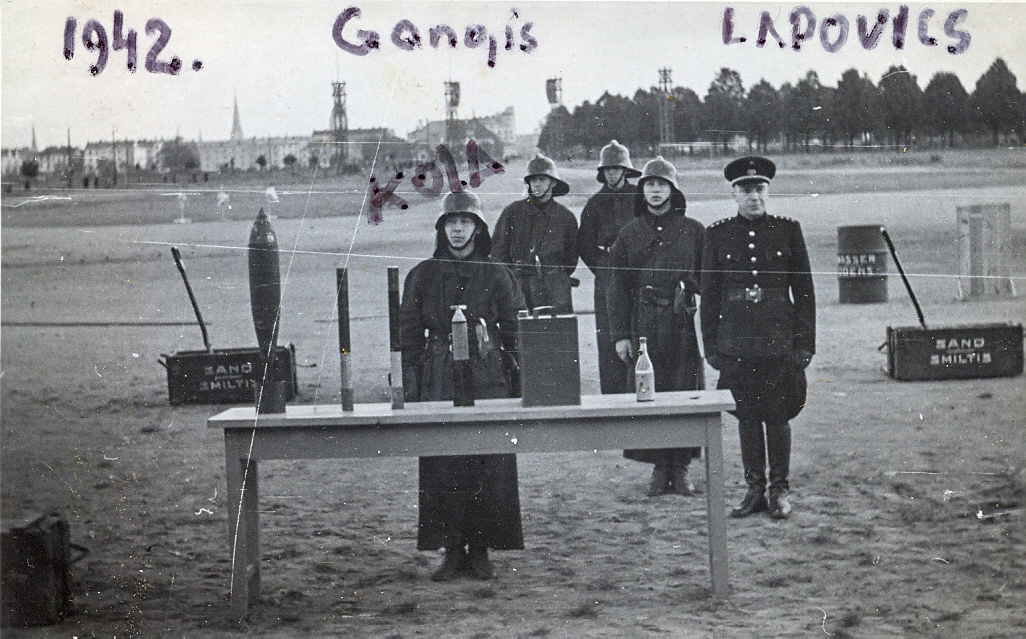
Historical sources of information on passive air defence during the German occupation (1942-1943) are rather scarce.
At training of neutralizing air bombs and incendiary bombs at Victory Square in Riga, Pardaugava, summer 1942
After the end of the Second World War, the passive air defense units of the Latvian SSR carried out post-war restoration works, and one of the most important measures in the interests of the civilian population was the clearing of the territory from mines, projectiles, of the unexplodeds aerial bombs and for other explosives, therefore the local population was involved in courses, trainings, also in demining works organized by OSAAVIAHIM (later renamed DOSAAF).
In order to strengthen the air defense, a decision of the LK(b)P Riga Committee Bureau of 14 November 1944 on local air defense was adopted, instructing to create air defense battalions, to provide telephone communications between the city defense headquarters and the districts, the most important object's and observation tower's.
In the 1950s, the Latvian SSR began intensive construction of civil protection management points, command posts, shelters and other defense facilities, with considerable investment.
On 1956 local anti-aircraft defense was included into state defense system. Its task was education of people on factors of threat of nuclear, chemical and biological weapons; to ensure the stable operation of national economy objects, carry out the necessary emergency and restoration work in the event of a nuclear threat.
Photo-stand for defense against nuclear weapons, late 1950s-1960s.
Transformation of local passive air defense into civil defense in 1961
On 1961 anti-aircraft defense system was transformed into civil defense, its main task was protection of inhabitants and economics in wartime and in peacetime catastrophes.
In case of nuclear attack or catastrophe it was envisaged to perform information of people, securing with shelters, during 12 hours provide with individual means of defense (gas-masks, children defense cameras, respirators), evacuation of people from towns to the country regions.
People were educated in civil defense, programs of civil defense were compulsory at schools, technical schools and higher educational establishments.
For securing work of economical branches and objects in case of war or catastrophe storing of material tehcnical means was organized- securing with water and energy resources, generators. For people working in largest enterprises shelters with all needed for several days and even weeks were built.
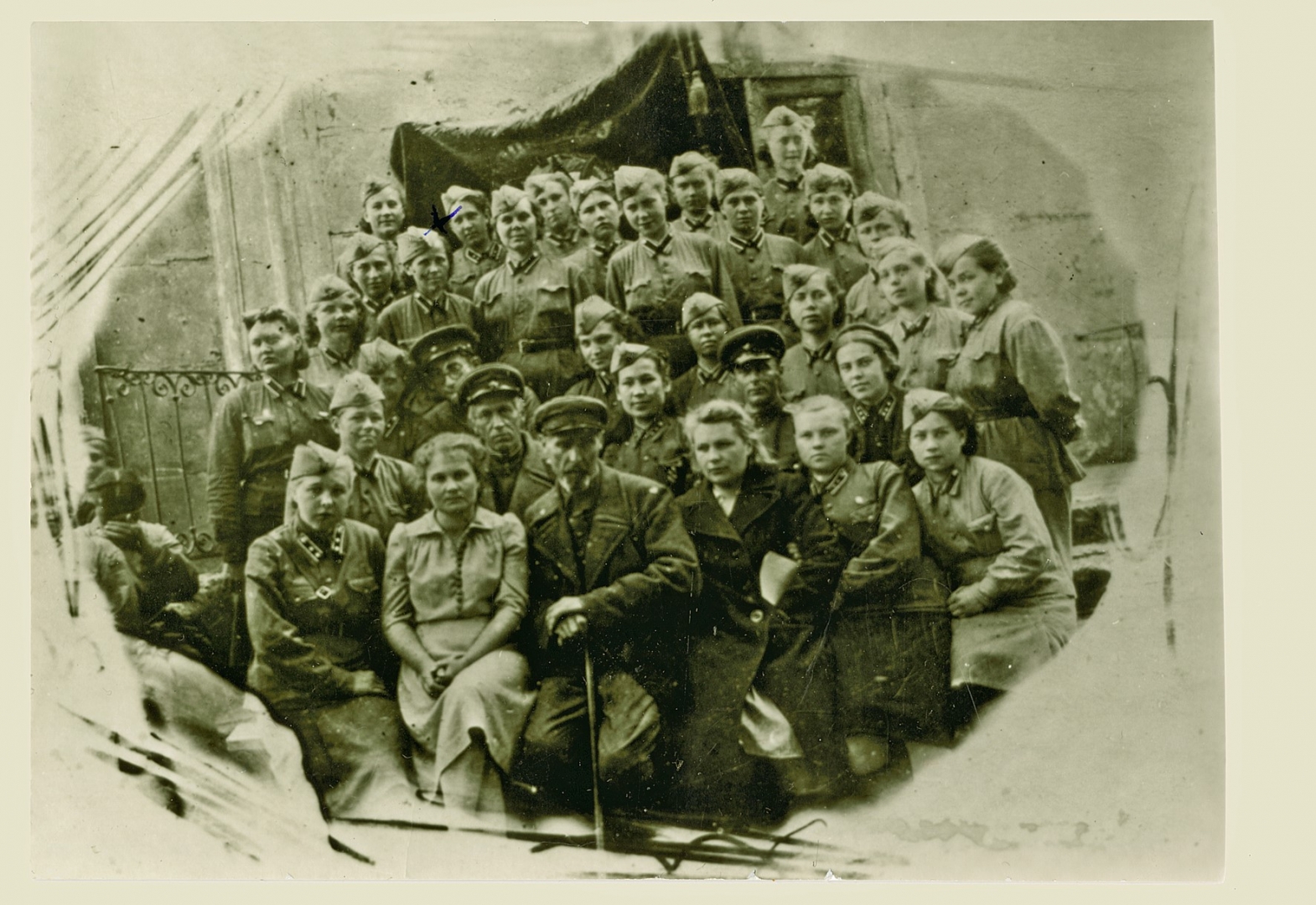
In Soviet times in Latvia, the chairman of the Council of Ministers was responsible for the operation of the civil defense system which was at the same time the chief of civil defense. Planning, organization and control of civil defense work was carried out by the Civil Defense Headquarters of the Latvian SSR, which was also operationally subordinate to the Baltic War Area. Heads of the objects were responsible for civil defense.
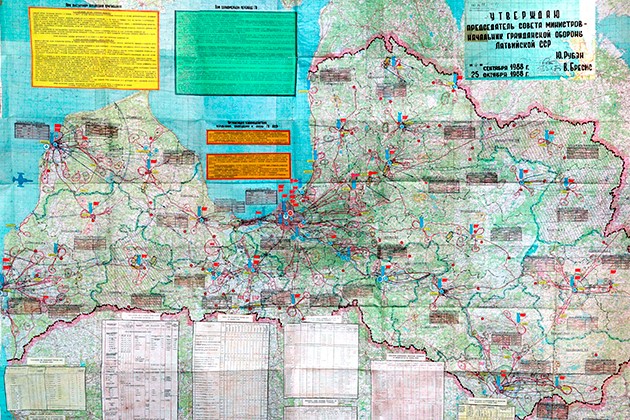
Latvian SSR Chief of Civil defense plan of work in wartime; Top secret Copy No 1, 1982
In state, local government services and companies, respective services were created and their main tasks for peacetime and wartime conditions were determined. Non-militarised civil defense formations and special formations were set up in the Services, according to the profile of the enterprise and the number of employees.
Each year civil defense trainings were organized in two cities and 5-6 regions of Latvia, but once in three years - state civil defense trainings were held. During the training, were prepared for the execution of the tasks the personnel of the civil defense formations.
Latvian SSR Kuldīga District civil defense Liaison Service work in the republican civil defense staff training, October 1966
Civil defense training of the Medical Service of Latvian SSR Valmiera district, 1987
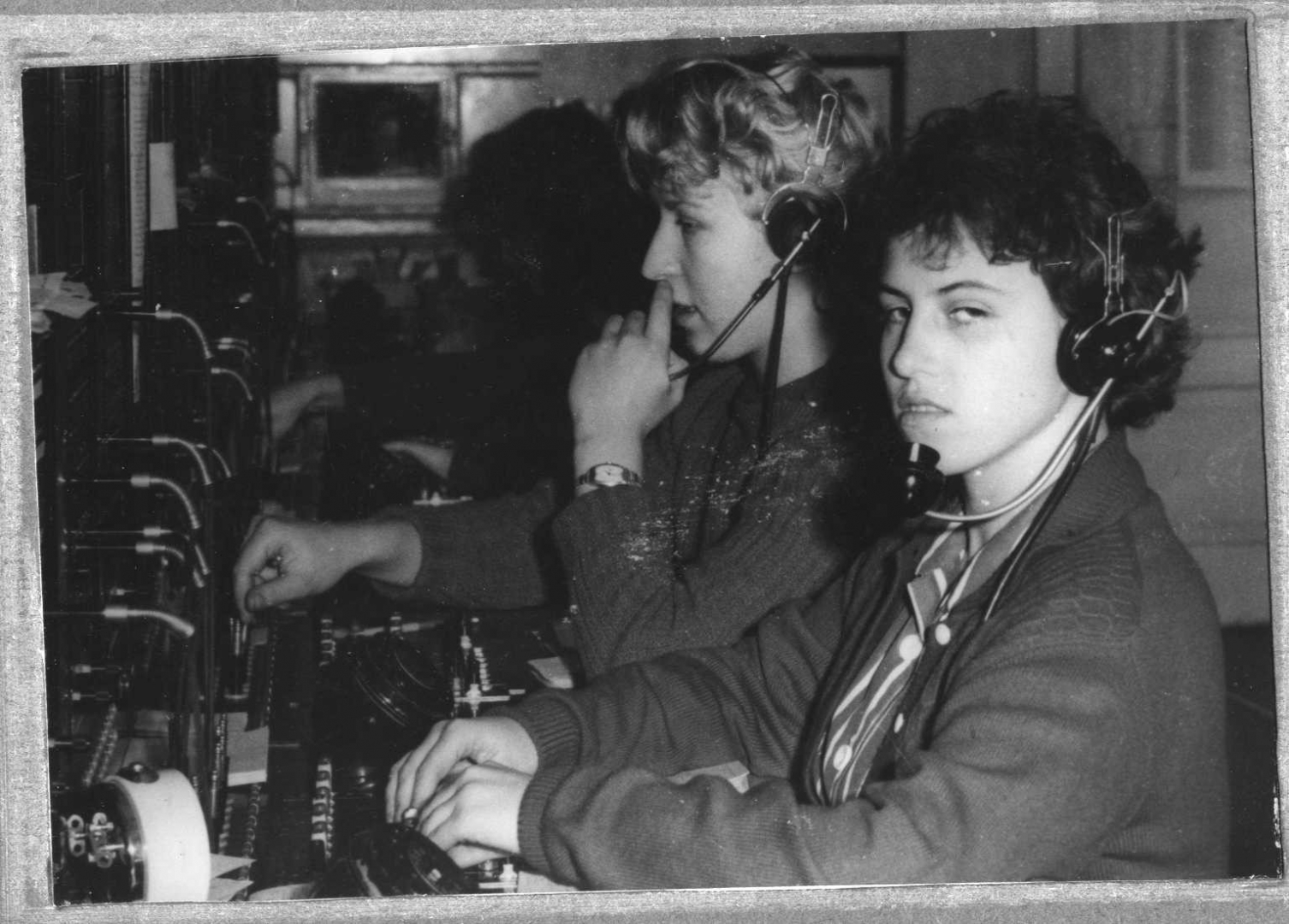
For announcing threat of war or catastrophe 1790 alarms, radio and television were used. One of the most effective information systems in the USSR of that times was introduced in Latvia on 1983-1986.
Alarms were switched on by civil protection headquarters in the country, regions and towns, at the same time information to inhabitants was given over the radio or television.
At enterprises of high risk local alarms and information systems were used for informing workers of those enterprises and people living in vicinity of them.
Single program radio network receiver Zenit-301, 1978
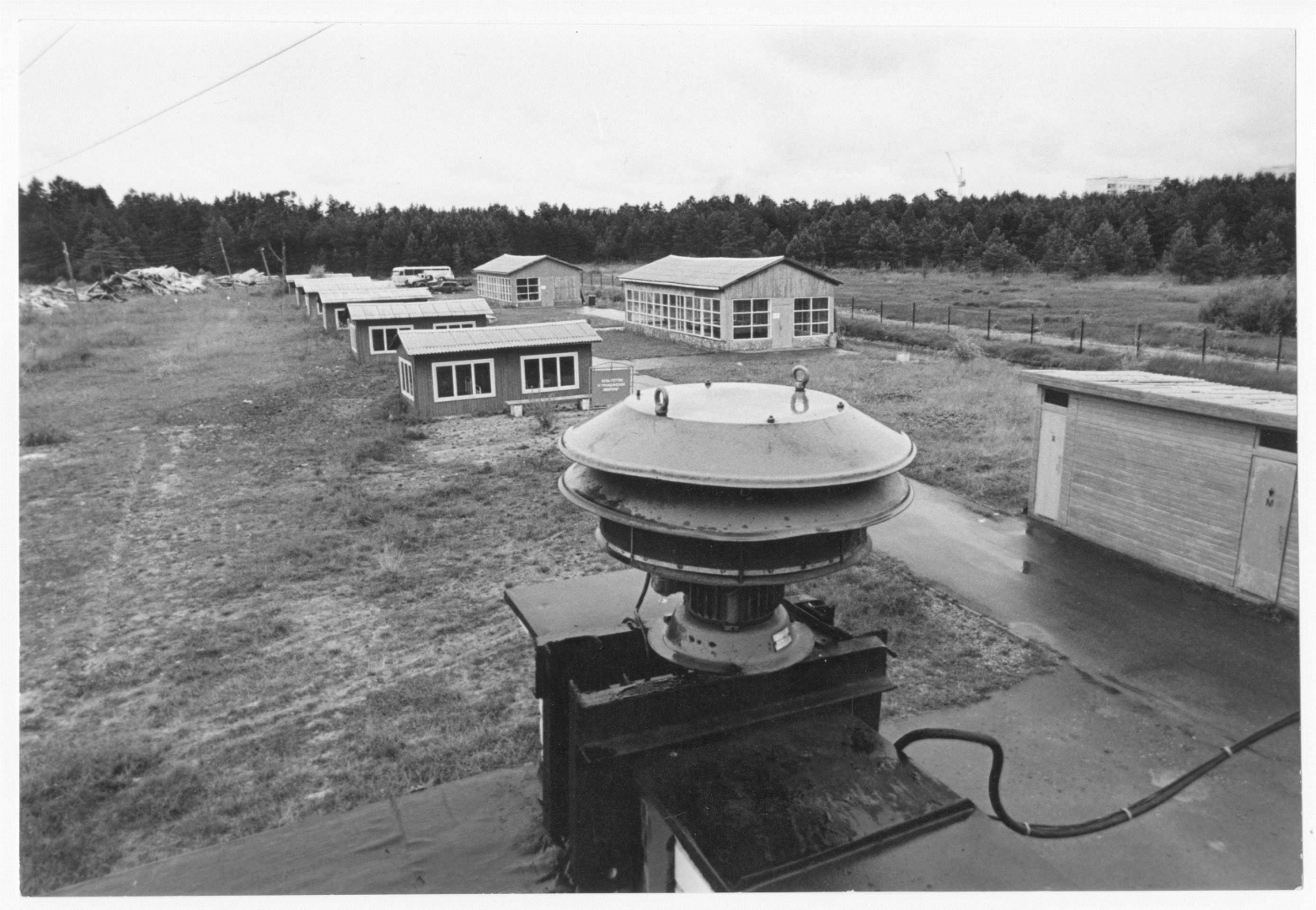
Civil protection training ground Suzi, Riga region for training of rescue in case of catastrophes, 1980s. In the foreground alarm S-40.
On 1991 reorganization of system of civil protection started. On the bases of Civil Protection Headquarters Civil Protection Strategic Center was formed. With the Decision of Supreme Cauncil of Republic of Latvia from 15 December 1992 it was renamed Civil Protection Center. On 15 December 1992 Law „About civil protection of Republic of Latvia” was passed. From 1993 Civil Protection Center worked under the guidance of Ministry of Defence, but from September 1996 it passed over to Ministry of Interior.
With the Amendment to the Law „About civil protection of Republic of Latvia” from 21 May 1998 civil protection system was integrated in State Fire and Rescue Service. On 31 July 1998 Emergency Preparedness Planning Department was formed. 0n 1 February 2006 it was renamed Civil Protection Department.
On 1 January 2007 the new Civil Protection Law entered into force, determining the structure, organization, main tasks, management, financing, tasks of state institutions, municipalities and merchants in the field of civil defense of the civil defense system (The law expired on October 1, 2016).
On October 1, 2016, the new Law on Civil Defense and Disaster Management entered into force, the purpose of which is to determine the legal and organizational principles of the operation of the civil defense system and disaster management in order to ensure the safety and protection of people, the environment, infrastructure and property as much as possible.